Sunday, February 2, 2025
Practical Aquaponics Ideas for Every Home Gardener
Practical Aquaponics Ideas for Every Home Gardener
Aquaponics, the symbiotic integration of aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil), offers a sustainable and efficient method for home food production. This article explores various practical aquaponics systems adaptable to diverse home gardening environments, emphasizing ease of implementation and maximized yield.
System Selection: Choosing the Right Aquaponics Setup for Your Home
The initial step involves selecting an aquaponics system appropriate for your space, experience level, and desired yield. Several configurations cater to various needs and limitations. Careful consideration of factors like available space, water supply, and time commitment is crucial for success.
Media Bed Systems: A Beginner-Friendly Approach
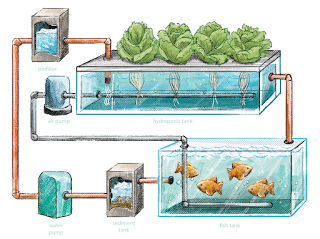
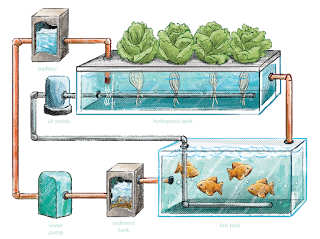
Media bed systems represent a popular entry point for novice aquaponics enthusiasts. These systems utilize a gravel or other inert media bed to support plant growth, where the water from the fish tank circulates, delivering essential nutrients. The simplicity of design and operation makes them ideal for beginners. A key advantage lies in their relative ease of maintenance and the robust nature of the plant support system. However, they require a larger footprint compared to other systems.
Advantages:
- Relatively simple to construct and maintain.
- Suitable for a wide variety of plants.
- Robust and less susceptible to certain issues compared to other systems.
Disadvantages:
- Requires significant space.
- Can be more challenging to manage water levels and oxygenation.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Systems: High-Yield, High-Maintenance
Deep water culture (DWC) systems suspend plants' roots directly in oxygenated nutrient-rich water. This method allows for rapid plant growth due to the constant access to nutrients and water. While offering high yields, DWC systems demand more diligent monitoring and maintenance to prevent root rot and ensure adequate oxygenation. They are better suited for more experienced aquaponic gardeners who can dedicate time to regular system checks and adjustments. Careful control of water temperature and pH is crucial.
Advantages:
- High yields and rapid plant growth.
- Relatively small footprint compared to media beds.
Disadvantages:
- Requires more frequent monitoring and maintenance.
- Higher risk of root rot if oxygenation or water quality is not properly managed.
- Generally less forgiving of errors compared to media bed systems.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Systems: Efficient Water Usage
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) systems deliver a thin film of nutrient-rich water directly to the plant roots, minimizing water usage and maximizing nutrient uptake. This method necessitates a precise and consistent water flow to avoid root drying. While highly efficient, NFT systems are more complex to construct and maintain, making them a better choice for individuals with prior aquaponics experience and a willingness to invest time in system monitoring. Careful plumbing and leak prevention are critical for success.
Advantages:
- Highly efficient water usage.
- Rapid plant growth due to excellent nutrient delivery.
Disadvantages:
- More complex to construct and maintain.
- Susceptible to clogs and requires diligent cleaning.
- Requires precise water flow control.
Choosing Your Fish and Plants: A Symbiotic Relationship
The selection of fish and plants significantly impacts the overall success of your aquaponics system. Compatibility is crucial, with certain fish species and plant types proving more conducive to a thriving ecosystem. Overstocking the fish tank can lead to detrimental consequences, while the incorrect plant choices can disrupt nutrient cycling.
Selecting the Right Fish Species
Hardy, fast-growing fish species are generally preferred for beginners. Tilapia, channel catfish, and goldfish are examples of relatively resilient options. However, research the specific requirements of your chosen species to ensure they thrive within your system. This includes considering factors such as water temperature, oxygen levels, and feeding schedules.
Plant Selection: Nutrient Uptake and Growth Rates
Leafy greens like lettuce, kale, and basil are excellent choices for aquaponics, as they have relatively high nutrient requirements and rapid growth rates. However, the range of plants suitable for aquaponics extends far beyond leafy greens. Consider your personal preferences and the nutritional requirements of each plant in relation to the fish waste produced in your system.
Building Your System: Step-by-Step Guide
Building an aquaponics system requires careful planning and execution. The specific steps will vary based on the chosen system type, but the overall process involves establishing the fish tank, constructing the grow bed (or setting up the DWC or NFT system), and connecting the two components via a reliable water circulation pump. Detailed instructions are readily available online and in specialized literature. Use food-grade materials to avoid contamination.
Essential Components: Pumps, Filters, and Media
A reliable water pump is vital for circulating water between the fish tank and the grow bed. Filters help remove solid waste from the water, maintaining water quality and preventing clogging. Media for media bed systems should be inert and provide ample surface area for beneficial bacteria colonization. Regular system maintenance involves cleaning the filters and checking the pump's operation.
Monitoring and Maintenance: Ensuring System Health
Regular monitoring and maintenance are paramount to maintaining a healthy and productive aquaponics system. Regular checks of water parameters, including pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, are crucial. These parameters directly influence the health of both the fish and the plants. Any deviations from optimal ranges should be addressed promptly. This may involve adjusting the feeding regime, changing the water, or addressing problems with the circulation system.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Preventing System Failures
Aquaponics systems can be subject to various challenges, including imbalances in nutrient levels, algae blooms, and fish diseases. Regular monitoring and preventive measures, such as proper filtration and adequate water changes, can mitigate many potential issues. Early detection and intervention are crucial in addressing any problems that arise. Refer to online resources and aquaponics communities for support in troubleshooting specific issues.
Conclusion: Embracing the Sustainable Harvest
Home aquaponics offers a sustainable and rewarding way to grow food and enjoy a connection with nature. While some initial investment and effort are required, the benefits of fresh, homegrown produce and the educational experience make it a worthwhile endeavor for many home gardeners. The detailed knowledge and careful planning addressed in this article can contribute significantly to the success of your aquaponics journey.
Sustainable Living Benefits Of Aquaponics Explained
Unlocking Sustainable Living: The Amazing Benefits of Aquaponics
Hey everyone! Let's talk about aquaponics. It sounds fancy, right? But trust me, it's way cooler than it sounds – and it's a game-changer when it comes to sustainable living. Basically, it's a symbiotic system where fish farming and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) come together in beautiful harmony. Think of it as a self-sustaining ecosystem, right in your backyard (or even your apartment!). And the best part? It's packed with benefits for both the planet and your plate.
Water Conservation: A Big Splash for Sustainability
One of the biggest wins with aquaponics is its incredible water efficiency. Traditional farming methods guzzle water – think about all the irrigation needed for vast fields. Aquaponics, however, recycles the water used in the fish tank to nourish the plants. The fish waste provides natural fertilizer, and the plants, in turn, filter the water, keeping it clean for the fish. This closed-loop system drastically reduces water consumption, making it a champion for water conservation in a world facing increasing water scarcity.
Less Water, More Food: The Aquaponic Advantage
Think about it: you're essentially creating a miniature, self-regulating ecosystem. The water that would normally be wasted goes straight back into the system. This means you're producing food with a fraction of the water used in traditional farming. It's a significant step towards more responsible and sustainable food production, especially in arid and semi-arid regions where water is a precious resource.
Reduced Fertilizer Use: Nature's Own Nutrient Solution
Conventional agriculture relies heavily on chemical fertilizers, which can be harmful to the environment. They pollute waterways, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, and can even damage soil health in the long run. Aquaponics takes a completely different approach. The fish waste, rich in nitrogen and other nutrients, acts as a natural fertilizer for the plants. No need for synthetic chemicals! This not only protects the environment but also results in healthier, more nutritious produce.
Cleaner Waterways, Healthier Ecosystems
By eliminating or drastically reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, aquaponics helps keep our waterways clean and protects aquatic life. Runoff from conventional farms often contaminates rivers and lakes, leading to harmful algal blooms and harming delicate ecosystems. Aquaponics offers a much more eco-friendly alternative, minimizing the impact on our precious water resources.
Increased Food Production in Smaller Spaces: Growing Food, Anywhere
Aquaponics systems are incredibly versatile. They can be scaled up or down to suit your needs and available space. Whether you have a sprawling backyard or a small balcony, you can set up an aquaponics system to grow your own food. This is a game-changer for urban farming and for people who want to access fresh, healthy food regardless of their living situation.
From Backyard to Balcony: The Adaptability of Aquaponics
Imagine growing your own tomatoes, lettuce, and herbs – alongside delicious fish – right outside your apartment window! Aquaponics makes this a reality. Its adaptability makes it a fantastic solution for communities with limited land, promoting food security and local food systems.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: A Greener Way to Grow
Conventional agriculture contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, mainly through the use of fossil fuels in machinery, transportation, and fertilizer production. Aquaponics, being a more localized and resource-efficient system, has a significantly lower carbon footprint. This means you're making a positive contribution to mitigating climate change by choosing this sustainable approach to food production.
Less Transportation, Less Pollution: Local Food, Local Impact
Because you're growing your food on-site, there's less need for long-distance transportation of produce. This reduces the fuel consumption and emissions associated with getting food from farm to table, creating a truly localized and sustainable food system.
Pest and Disease Control: A Naturally Balanced System
Aquaponics systems are naturally less susceptible to pest infestations and diseases compared to traditional farming. The closed-loop system helps prevent the spread of pests and diseases, minimizing the need for pesticides and other harmful chemicals. This contributes to safer, healthier food and a healthier environment.
Natural Resistance: A Healthier Approach
The balanced ecosystem within the aquaponic system creates a natural resistance to many common pests and diseases. This reduces the reliance on harmful chemical interventions, making it a more sustainable and responsible way to grow food.
Fresh, Nutritious Food: Homegrown Goodness
Let's not forget the most rewarding aspect: delicious, fresh, and nutritious food! Knowing exactly where your food comes from and how it's grown is incredibly satisfying. You'll have access to high-quality, homegrown produce and fish, boosting both your health and your sense of accomplishment.
From Seed to Plate: The Joy of Homegrown Food
The taste of freshly harvested vegetables and sustainably raised fish is unparalleled. The satisfaction of growing your own food is a rewarding experience that connects you to the natural world and promotes healthier eating habits.
Commonly Asked Questions
- Is aquaponics difficult to set up? The complexity depends on the scale of your system. Smaller, beginner-friendly systems are readily available, and plenty of online resources and communities can guide you through the process.
- What kind of fish can I use in an aquaponics system? Tilapia, catfish, and koi are popular choices, but the best fish for your system will depend on your climate and the size of your setup. Research is key!
- How much space do I need? Aquaponics systems can be adapted to various spaces, from small tabletop systems to larger outdoor setups. Consider your available space and your desired yield when choosing a system size.
- What about maintenance? Aquaponics systems require regular monitoring and maintenance, including water testing, cleaning, and occasional adjustments to the system's balance. The amount of maintenance depends on the size and complexity of your system.
- Is aquaponics expensive? The initial investment can vary widely depending on the size and complexity of your system. However, the long-term savings in water, fertilizer, and other resources can make it a cost-effective solution over time.
- Can I grow any type of plant? Many plants thrive in aquaponic systems, including leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, peppers, and even some fruiting plants. However, some plants may require more specific conditions than others.
So there you have it! Aquaponics offers a compelling path towards a more sustainable and fulfilling lifestyle. It's a rewarding experience that combines the joys of gardening and fish keeping while contributing to a healthier planet. Why not give it a try? You might just be amazed at what you can grow!
Organic Aquaponics Gardening For Urban Environments
Organic Aquaponics Gardening for Urban Environments
Imagine a vibrant, self-sustaining food source nestled within the concrete jungle of your city. This isn't science fiction; it's the reality of organic aquaponics, a revolutionary gardening method perfectly suited for urban spaces. Aquaponics cleverly combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation) to create a closed-loop ecosystem teeming with life and producing fresh, organic food. This symbiotic relationship minimizes waste, maximizes resource use, and offers a sustainable and rewarding gardening experience, even in the most limited of urban environments.
The Science Behind the Synergy
Aquaponics thrives on the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. Fish produce waste, primarily ammonia. Beneficial bacteria, housed within the system's biofilter, convert this toxic ammonia into nitrites, then into nitrates. These nitrates are the essential nutrients plants crave to flourish. The plants, in turn, filter the water, removing excess nutrients and providing a clean, healthy environment for the fish. This elegant cycle requires careful monitoring and balancing, but the rewards are significant: a continuous, self-regulating ecosystem producing both delicious fish and nutrient-rich vegetables.
Choosing the Right System for Your Urban Space
The beauty of aquaponics lies in its adaptability. Whether you have a rooftop terrace, a balcony, or even a sunny windowsill, you can find an aquaponics system that fits your space. Media bed systems utilize gravel or other inert materials as a growing medium, providing a simple and effective solution for beginners. Deep water culture (DWC) systems, where plant roots hang directly in nutrient-rich water, are ideal for maximizing space and yield. Nutrient film technique (NFT) systems, using a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over plant roots, offer another efficient option for urban growers. Carefully consider your available space, time commitment, and desired crop selection when choosing your system.
Setting Up Your Urban Aquaponics Garden
Establishing your urban aquaponics garden involves several key steps. First, you'll need to select the appropriate system, procure the necessary equipment (tanks, pumps, grow beds, tubing, etc.), and choose your fish and plants wisely. Hardy, fast-growing plants like lettuce, basil, and tomatoes are excellent choices for beginners. Similarly, tilapia and goldfish are known for their hardiness and compatibility with aquaponics systems. Remember to thoroughly research the specific needs of your chosen species to ensure their health and thriving in your system.
Essential Considerations for Organic Aquaponics
Maintaining organic certification in your aquaponics system necessitates careful attention to detail. You must use organic fish feed free from antibiotics and synthetic chemicals. Avoid using synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, opting instead for natural pest control methods such as beneficial insects or companion planting. Regularly monitor water parameters (pH, ammonia, nitrite, nitrate levels) to ensure a healthy environment for both fish and plants. This commitment to organic practices not only guarantees the health of your produce but also contributes to a healthier planet.
Harvesting Your Urban Bounty
The final, and arguably most rewarding, stage is harvesting your homegrown produce. Enjoy the fresh, organic fish and vegetables you've cultivated. Aquaponics provides an opportunity to reconnect with your food source, understanding its journey from seed to table. The satisfaction of nurturing life and harvesting your own food is unparalleled, making organic urban aquaponics a deeply rewarding experience. Share your bounty with friends, family, and neighbors, promoting sustainable food practices within your community. This process isn't just about growing food; it's about cultivating a more sustainable and connected urban lifestyle.
Beyond the Basics: Expanding Your Urban Aquaponics
As your confidence grows, you can explore more advanced techniques. Experiment with different plant varieties, optimize your system for maximum yield, and consider incorporating vertical gardening techniques to maximize space utilization. You might even integrate solar power to reduce your environmental impact further. The possibilities are virtually endless, making aquaponics a constantly evolving and engaging endeavor for urban gardeners.
Affordable Aquaponics Kits for Urban Gardeners
Affordable Aquaponics Kits for Urban Gardeners: A Comprehensive Guide
The burgeoning interest in sustainable food production has propelled aquaponics, a symbiotic system combining aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil), into the spotlight. While traditionally perceived as a large-scale endeavor, the advent of affordable aquaponics kits has democratized this practice, making it accessible to urban gardeners with limited space and resources. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these kits, focusing on their affordability, features, and suitability for various urban gardening contexts.
Understanding the Appeal of Aquaponics Kits
Aquaponics offers several compelling advantages for urban dwellers, particularly those seeking self-sufficiency and environmentally conscious food production. The integrated nature of the system minimizes water waste – a critical factor in urban environments often facing water scarcity. Furthermore, aquaponics eliminates the need for large quantities of soil, a significant benefit for apartment dwellers or those with limited garden space. The system's self-sustaining nature also reduces the reliance on chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting healthier food production.
Key Benefits of Aquaponics for Urban Settings:
- Space Efficiency: Aquaponics systems can be adapted to fit various spaces, from small balconies to rooftops.
- Water Conservation: Recirculating water systems significantly reduce water usage compared to traditional gardening.
- Reduced Reliance on External Inputs: The closed-loop nature minimizes the need for fertilizers and pesticides.
- Year-Round Production (with proper climate control): Indoor aquaponics systems allow for consistent food production regardless of the season.
- Enhanced Food Security: Provides a source of fresh, healthy produce.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Affordable Aquaponics Kit
Selecting the right aquaponics kit requires careful consideration of several factors, balancing affordability with functionality and long-term sustainability. A thorough assessment of your space, budget, and gardening experience will guide your decision-making process.
Budgetary Constraints:
Affordable aquaponics kits vary significantly in price. While some basic kits might be available for under $100, more advanced systems with features like automated water pumps and filtration can cost considerably more. Setting a realistic budget before commencing your search is crucial. Consider the long-term costs associated with maintenance, fish food, and potential repairs.
System Size and Capacity:
The size of the system directly impacts the quantity of fish and plants you can cultivate. Beginners might find smaller kits more manageable, allowing them to learn the intricacies of the system without overwhelming investment. Larger systems offer greater potential for yield but require more space and maintenance.
System Components and Features:
Examine the included components carefully. Essential elements include a fish tank, grow bed (media bed or deep water culture), water pump, air pump (often essential for fish health), and tubing. Consider features like automated water level control, built-in filtration, and grow lights (if planning indoor cultivation). Some kits offer modular designs, permitting expansion as your experience grows.
Ease of Assembly and Maintenance:
Opt for kits with clear instructions and straightforward assembly processes. Regular maintenance is vital for a healthy aquaponics system. Choose a kit that's easy to clean and maintain, minimizing the time and effort required for upkeep. Consider the availability of replacement parts, should any components fail.
Type of Aquaponics System:
Aquaponics kits generally fall into two main categories: media bed systems and deep water culture (DWC) systems. Media bed systems use gravel or other inert media to support plant roots, while DWC systems suspend plant roots directly in nutrient-rich water. Each system has its pros and cons concerning ease of maintenance, plant types suitable for growth, and initial setup cost. Research both types to determine which aligns best with your skills and preferences.
Examples of Affordable Aquaponics Kits
The market offers a diverse range of affordable aquaponics kits catering to various needs and budgets. While specific products and their availability fluctuate, the following categories illustrate the types of kits available:
Beginner Kits:
These typically include smaller tanks, simpler designs, and fewer features. They are ideal for those new to aquaponics, providing a low-risk entry point into the practice. They generally focus on ease of use and maintenance above large-scale yields. Expect limited capacity in terms of fish and plants.
Intermediate Kits:
Intermediate kits offer a balance between affordability and functionality. They might incorporate features like automated water pumps or more sophisticated filtration systems. These kits are suitable for those with some experience in gardening and aquaponics who desire a more robust and productive system.
DIY Kits:
Several vendors provide DIY kits containing essential components, requiring users to assemble the system. This approach can be more economical but demands more time, skill, and effort. It allows for greater customization but might present challenges for novices.
Add-on Components:
Many vendors also offer add-on components such as additional grow lights, larger tanks, or more efficient pumps. These additions can enhance the functionality of existing kits, allowing for customization and expansion as the user's needs evolve.
Beyond the Kit: Essential Considerations for Success
While an affordable aquaponics kit forms the foundation of your system, success hinges on several additional factors beyond the initial purchase. Careful planning and diligent management are crucial for a thriving system.
Fish Selection:
Choose hardy and adaptable fish species well-suited to the confines of your system. Tilapia and goldfish are popular choices for beginners due to their tolerance for varying water conditions. Research specific species' requirements regarding water temperature, pH levels, and oxygenation.
Plant Selection:
Select plants that thrive in the slightly alkaline and nutrient-rich water of the aquaponics system. Leafy greens, herbs, and some fruiting vegetables are often good choices. Avoid plants with exceptionally high nutrient demands in the beginning stages.
Water Quality Monitoring:
Regular monitoring of water parameters, including pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, is essential. These parameters influence the health of both the fish and the plants. Regular water changes might be necessary, depending on the system's design and capacity.
Maintenance and Cleaning:
Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial to prevent the buildup of harmful substances and to ensure the proper functioning of the system. This includes cleaning the grow bed, changing water (partially or completely depending on the system), and checking equipment functionality.
In conclusion, affordable aquaponics kits present a viable pathway for urban dwellers to engage in sustainable food production. Careful consideration of the factors outlined above, coupled with diligent management and ongoing learning, will significantly enhance the chances of establishing a thriving and productive aquaponics system within the confines of an urban setting.
Energy Efficient Aquaponics Setup Ideas For Savings
Energy-Efficient Aquaponics System Design for Optimized Resource Utilization and Cost Savings
Aquaponics, the symbiotic integration of aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil), offers a sustainable and productive food production method. However, energy consumption can be a significant factor influencing the overall cost-effectiveness of an aquaponics system. This article explores various strategies for designing and operating energy-efficient aquaponics setups, focusing on minimizing energy expenditure while maximizing yield and resource utilization.
Optimizing System Design for Reduced Energy Consumption
The foundation of an energy-efficient aquaponics system lies in careful planning and design. Several key aspects contribute to minimizing energy use throughout the system's operational lifespan.
1. System Location and Orientation: Harnessing Natural Resources
Strategic system placement can significantly reduce energy demands. Optimal sunlight exposure minimizes the need for supplemental lighting in plant growth areas. South-facing systems (in the Northern Hemisphere) benefit from maximum solar radiation. Careful consideration should also be given to ambient temperature. Positioning the system in a sheltered location reduces temperature fluctuations, minimizing the energy required for heating or cooling. This reduces reliance on energy-intensive climate control systems.
2. Water Management: Reducing Pumping and Filtration Needs
Water circulation is crucial in aquaponics, but excessive pumping consumes significant energy. Minimizing the distance water needs to travel between the fish tank, grow beds, and other system components reduces energy expenditure. The use of gravity-fed systems wherever feasible is a highly energy-efficient approach. Efficient pump selection is critical. High-efficiency pumps with low power consumption should be prioritized. Regularly cleaning and maintaining pumps to prevent clogging also optimizes their performance and prolongs their lifespan.
Effective filtration is crucial for maintaining water quality, but overly complex or energy-intensive filtration systems should be avoided. A well-designed system incorporating biofiltration (using beneficial bacteria to break down waste) and mechanical filtration (removing larger solids) can significantly reduce the need for energy-intensive mechanical filtration methods.
3. Insulation and Thermal Management: Minimizing Climate Control Energy
Fluctuations in ambient temperature can significantly impact system performance and energy consumption. Insulating the system components, particularly the fish tank and grow beds, helps maintain a stable temperature, reducing the energy required for heating or cooling. Materials such as foam insulation or recycled materials can be used to insulate the system effectively and minimize heat loss or gain. The use of passive solar heating or cooling techniques can further enhance energy efficiency.
4. Choosing Appropriate Lighting: Optimizing Plant Growth with Minimal Energy
Supplemental lighting is often necessary, especially in environments with limited sunlight. However, the type of lighting selected greatly affects energy consumption. LED grow lights are considerably more energy-efficient than traditional fluorescent or high-pressure sodium lamps. Additionally, careful consideration of the light spectrum and intensity required by the chosen plants can optimize growth while reducing unnecessary energy use.
Integrating Renewable Energy Sources: Sustainable Power Solutions
The integration of renewable energy sources can dramatically reduce the environmental impact and operating costs of an aquaponics system. Several options are available, each with its own set of advantages and limitations.
1. Solar Energy: Harnessing the Sun's Power
Solar panels can provide a clean and renewable energy source for powering the aquaponics system. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, eliminating the need for grid power. The size of the solar array will depend on the system's energy requirements and the amount of available sunlight. Battery storage can be integrated to ensure a continuous power supply, even during periods of low sunlight.
2. Wind Energy: Utilizing Wind Power for System Operation
In areas with consistent wind, wind turbines can be a viable option for generating electricity to power the aquaponics system. The size and capacity of the turbine will depend on the average wind speed and the system's energy demand. However, wind energy is often less reliable than solar energy, and appropriate backup power sources may be required.
3. Geothermal Energy: Utilizing Earth's Heat
Geothermal energy can be used for heating or cooling the aquaponics system. Ground source heat pumps can efficiently transfer heat from the earth to the system in winter and vice-versa in summer. This approach requires an initial investment in the geothermal system, but it can result in substantial long-term energy savings.
Implementing Energy-Saving Practices: Operational Efficiency
Beyond system design, operational practices play a significant role in minimizing energy consumption.
1. Regular System Maintenance: Optimizing Performance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal system performance and minimizing energy waste. This includes cleaning filters regularly to prevent clogging and reduce the load on pumps, checking pump efficiency and addressing any leaks promptly, and ensuring that all components are functioning optimally. Routine maintenance prevents unnecessary energy consumption caused by inefficient or faulty equipment.
2. Monitoring and Data Logging: Identifying Areas for Improvement
Monitoring key parameters such as water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen levels, and energy consumption can help identify areas for improvement. Data logging systems can provide valuable insights into system performance, enabling adjustments to optimize energy use. Smart sensors and automated control systems can further improve efficiency by automatically adjusting parameters based on real-time data.
3. Efficient Water Usage: Reducing Evaporation and Water Loss
Minimizing water loss through evaporation can reduce the energy needed for water replacement and temperature control. Covering the grow beds with lids or using a closed-loop system can significantly reduce evaporation. Regular checks for leaks and timely repairs are also essential to minimize water loss and subsequent energy expenditure.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Sustainable Aquaponics
Designing and operating an energy-efficient aquaponics system requires a holistic approach, encompassing careful system design, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the implementation of energy-saving operational practices. By prioritizing energy efficiency from the outset, aquaponics can become an even more sustainable and cost-effective method of food production, promoting both environmental responsibility and economic viability.
Organic Aquaponics Methods for Small Gardens
Organic Aquaponics Methods for Small Gardens
Aquaponics, the symbiotic integration of aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (soil-less plant cultivation), offers a sustainable and efficient method for food production, particularly well-suited to small garden spaces. This article explores organic aquaponics techniques tailored for compact environments, emphasizing ecological balance and minimizing environmental impact.
System Design for Small-Scale Organic Aquaponics
The success of any aquaponics system, especially a small-scale one, hinges on careful system design. Several factors need meticulous consideration to optimize both fish and plant health within limited space.
Choosing the Right System Type
Several aquaponics system designs exist, each with advantages and disadvantages related to space constraints. For small gardens, media bed systems and deep water culture (DWC) systems are particularly popular due to their compact nature.
- Media Bed Systems: These systems utilize a bed filled with gravel, clay pebbles, or other inert media to support plant growth. The nutrient-rich water from the fish tank is circulated through the media bed, providing essential nutrients to the plants. Smaller systems can be built using readily available materials such as repurposed containers and readily available media. They are relatively low-maintenance and suitable for beginners.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) Systems: In DWC systems, plant roots hang freely in oxygen-rich water. A small air pump provides constant aeration, ensuring sufficient oxygen for root health. This method requires less space than media bed systems for the same plant yield but demands more attention to water quality and oxygen levels. This is a more advanced system.
Tank Selection and Size
The size of the fish tank directly influences the system's capacity. For a small garden, a tank holding 20-50 gallons is a practical starting point. Smaller tanks necessitate more frequent water changes and careful monitoring of water parameters. The material of the tank should be non-toxic and food-safe, such as food-grade plastic or fiberglass. Avoid using materials that could leach harmful chemicals into the water.
Plant Selection for Organic Aquaponics
Selecting appropriate plants is crucial for a thriving system. Choose plants known for their vigorous growth and ability to tolerate a slightly variable nutrient supply. Leafy greens, herbs, and some fruiting vegetables perform well in aquaponics.
- Leafy Greens: Lettuce, spinach, kale, and arugula are excellent choices due to their rapid growth and high nutrient uptake.
- Herbs: Basil, mint, chives, and parsley thrive in aquaponics and can be easily incorporated into a small garden setting.
- Fruiting Vegetables: Tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries can be grown, although they require more space and attention.
Fish Selection
The choice of fish species significantly impacts the system's success. Selecting a species adapted to the tank size and water temperature is essential. Tilapia and trout are popular choices, though specific requirements vary. Consider the bioload – the amount of waste produced by the fish – to avoid overwhelming the system's capacity for nutrient processing. Begin with a smaller number of fish and gradually increase the population as the system matures.
Organic Principles in Aquaponics
Organic aquaponics emphasizes sustainability and minimizes the use of synthetic inputs. This approach fosters a healthy ecosystem that relies on natural processes for nutrient cycling and pest control.
Nutrient Cycling and Beneficial Bacteria
The core of any aquaponics system is the nitrification cycle. Beneficial bacteria convert fish waste (ammonia) into nitrite and then nitrate, which plants can absorb as nutrients. Maintaining a healthy population of these bacteria is paramount. Avoid using chemical treatments that could kill these beneficial bacteria. A mature system will naturally develop a robust bacterial community.
Organic Fertilization
While fish waste provides a significant source of nutrients, supplemental organic fertilization can enhance plant growth. Compost tea, worm castings, or other organic fertilizers can be introduced into the system to boost nutrient levels without compromising the organic integrity.
Pest and Disease Management
Organic pest and disease control relies on natural methods. Beneficial insects, companion planting, and careful monitoring can prevent infestations and disease outbreaks. Avoid using synthetic pesticides or herbicides, as they can harm the fish and beneficial bacteria within the system.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial for a healthy and productive organic aquaponics system. This involves checking key parameters and performing routine tasks.
Water Quality Monitoring
Regular testing of water parameters, including pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, is essential. Maintaining the appropriate balance of these parameters ensures the health of both fish and plants. Use a reliable test kit to monitor these regularly.
Water Changes
While less frequent than in traditional aquaculture, periodic water changes are still necessary to remove accumulated solids and maintain optimal water quality. The frequency depends on the system's size and fish stock. Water changes should be performed carefully to minimize disruption to the system's delicate balance.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning of the system is essential to prevent the build-up of algae and debris. Cleaning should be done carefully to avoid harming the beneficial bacteria. Removing accumulated solids from the bottom of the tank and cleaning the grow bed will help maintain optimal conditions for plant growth.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with careful planning and maintenance, problems can arise in aquaponics systems. Common issues include:
- High Ammonia Levels: Overstocking, insufficient filtration, or a malfunctioning system can lead to high ammonia levels. Address this by reducing fish stock, improving filtration, and checking for equipment problems.
- Low pH: Low pH can harm fish and plants. Adjust pH slowly and carefully using appropriate organic methods, such as adding crushed coral or limestone.
- Algae Blooms: Excessive light or nutrient build-up can cause algae blooms. Reduce light exposure, and maintain water quality.
By carefully considering the principles outlined above, small-scale organic aquaponics can provide a rewarding and sustainable method of growing food within the constraints of a small garden. Remember that patience, observation, and a willingness to adapt are essential for success. A successful aquaponics system requires a delicate balance and careful management, but the benefits of fresh, organically grown food make it a worthwhile endeavor. Through diligent attention to detail and a commitment to organic practices, small gardens can thrive with this integrated system.
Sustainable Living Made Easy with Aquaponics Benefits
Sustainable Living Made Easy with Aquaponics Benefits
Hey everyone! So you're interested in sustainable living, huh? That's awesome! It can feel overwhelming at first, figuring out where to even start. But what if I told you there's a surprisingly simple, yet incredibly effective way to grow your own food and reduce your environmental impact? Enter aquaponics! This isn't some futuristic, complicated system; it's actually a pretty cool blend of aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil). Let's dive in and explore how aquaponics can make sustainable living easier than you think.What is Aquaponics, Anyway?
Imagine a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants – that's essentially what aquaponics is all about. Fish waste, which is rich in ammonia, is naturally filtered by beneficial bacteria in the system. These bacteria convert the ammonia into nitrites, then nitrates – a fantastic natural fertilizer for your plants! The plants, in turn, filter the water, keeping it clean and healthy for the fish. It's a closed-loop system, meaning you use significantly less water than traditional gardening and minimize waste. Pretty neat, right?
The Amazing Benefits of Aquaponics
There are so many reasons why aquaponics is gaining popularity as a sustainable living solution. Let's highlight some key benefits:
Reduced Water Consumption:
This is a huge one! Traditional agriculture uses tons of water. Aquaponics, because of its closed-loop system, recycles water, significantly reducing your water footprint. You're essentially creating a mini-ecosystem that conserves precious resources.
Year-Round Growing Potential (depending on your setup):
Depending on where you live and the type of aquaponics system you choose, you can grow food all year round! No more waiting for the right season – you can have fresh herbs, vegetables, and even fruits year-round, greatly increasing your food security.
Less Reliance on Chemical Fertilizers and Pesticides:
Aquaponics uses the natural waste from fish to fertilize the plants. This eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers, which can harm the environment and your health. Similarly, the closed system minimizes pest problems, reducing or eliminating the need for harmful pesticides.
Fresh, Healthy Food:
You'll know exactly where your food comes from, ensuring its freshness and quality. Plus, you can control what goes into your system, avoiding harmful chemicals and GMOs. The satisfaction of harvesting your own food is unbeatable!
Reduced Food Miles:
By growing your own food, you dramatically cut down on the transportation needed to get food from farm to table. This reduces your carbon footprint and supports local food systems.
Great for Beginners:
While it might sound complex initially, aquaponics is surprisingly accessible for beginners. There are many resources and tutorials available online and plenty of communities dedicated to helping newcomers get started. You can start small and scale up as you gain experience.
Different Types of Aquaponics Systems
There's no one-size-fits-all when it comes to aquaponics. Different systems suit different needs and spaces:
Media Bed Systems:
These are among the most common and beginner-friendly systems. They use a bed filled with gravel or clay pebbles where the plants are grown, and the water from the fish tank is circulated through this bed.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Systems:
In DWC systems, the plant roots hang directly in the nutrient-rich water. This is a highly efficient system, but it requires more careful monitoring of water levels and oxygenation.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Systems:
NFT systems use a thin film of nutrient-rich water that flows over the roots of the plants. This is a more advanced system but very efficient in terms of space and water usage.
Hybrid Systems:
Many aquaponics enthusiasts combine elements of different systems to create a custom setup that best fits their needs and resources.
Getting Started with Your Own Aquaponics System
Ready to take the plunge? Here's a simplified roadmap to get you started:
Commonly Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about aquaponics:
Q: How much does it cost to set up an aquaponics system?
A: The cost varies greatly depending on the size and complexity of your system. You can start with a relatively inexpensive setup or invest in a more sophisticated system for a larger scale operation.
Q: How much space do I need?
A: Again, this depends on the size of your system. You can have a small indoor system on a balcony or a larger outdoor system in your backyard.
Q: How much time does it take to maintain an aquaponics system?
A: Maintenance requirements vary depending on the size and type of your system. A smaller system might require 15-30 minutes of care per week, while a larger system could need more time.
Q: What kind of fish can I use?
A: Tilapia, goldfish, and catfish are popular choices for beginners due to their hardiness. Research is key to selecting the right species for your climate and system.
Q: What plants grow well in aquaponics?
A: Leafy greens, herbs, and some fruiting vegetables thrive in aquaponics. Experiment to discover what works best in your specific system.
So there you have it! Aquaponics is a fantastic way to embrace sustainable living, enjoy fresh, healthy food, and reduce your environmental impact. It might seem like a big commitment, but with a bit of research and a willingness to learn, you can easily grow your own food in a fun and rewarding way. Happy growing!